On July 5th, WeLegal joined hands with King&Capital Law Firm to share and exchange views with more than 30 legal directors and heads of legal affairs of famous enterprises on the topic of "Prevention and Control of Risks in Executives' Performance of Duties". The event provided in-depth explanations on "Prevention of Criminal Legal Risks in Executives' Performance of Duties and Construction of Anti-Bribery Compliance Management System", "Duty of Care and Risk Isolation of Directors and Supervisors of a Company - Viewing from the Perspective of Cases of Listed Companies", and "Legal Risks Related to Transfer of Benefits from the Same Kind of Businesses of Executives of a Company". 30-odd executives of listed companies and heads of legal affairs and compliance participated in the event. compliance officers of listed companies attended the seminar.
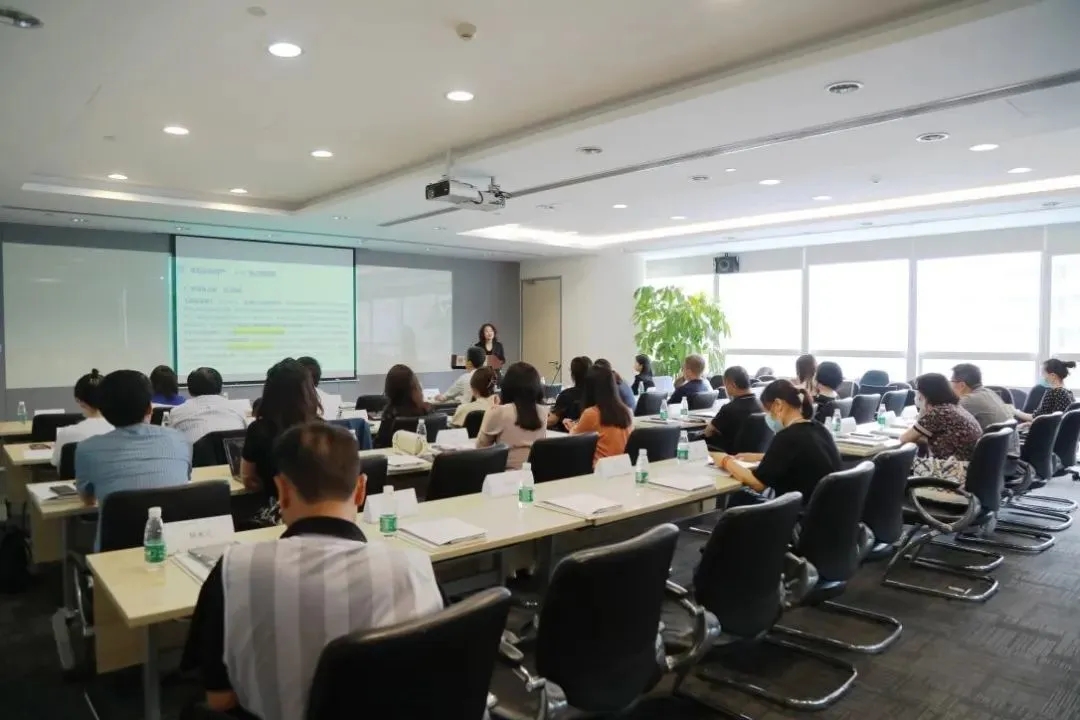

Scene of the event
I
Prevention of Criminal Legal Risks in Executives' Performance of Duties and Construction of Anti-Bribery Compliance Management System

Ms. Liang Yali
Liang Yali, Senior Partner of King&Capital Law Firm and Director of King&Capital Criminal Research Center, spoke about the newly revised Securities Law in 2020, which not only redefines the standards of information disclosure, but also reconstructs the legal responsibility for information disclosure violations. According to relevant statistics, in 2020 and 2021, the Securities and Futures Commission handled 740 and 609 cases respectively, of which 177 and 116 cases (clues) of suspected crimes were transferred to public security organs according to the law, and the number of cases (clues) of suspected crimes transferred to public security organs according to the law in 2021 increased by 53% year-on-year.
The new Securities Law provides for greater regulation of disclosure violations, and the rise in the number of suspected criminal cases (clues) to be transferred to the public security authorities by the SEC in 2020 and 2021 is a signal that the SEC's determination to comprehensively implement the "zero tolerance" approach is consistent, and the country is increasing the cost of corporate directors and supervisors violating the law and committing crimes. The State's direction to increase the cost of corporate directors and supervisors for violating the law and committing crimes has become clearer. Under the turbulent market conditions, in the face of the huge interests of the capital market, we cannot rely solely on moral restraints, nor can we test the purity of human nature, but we must rely on strict legal provisions and heavy regulatory policies to force the directors and supervisors of the company to perform their duties to enhance their capacity and awareness of compliance.
In the normal operation of the company, company directors and supervisors often do not pay attention to the relevant legal provisions and compliance requirements, but in the event of major lawsuits and disputes or compliance loopholes triggering accountability, company directors and supervisors have to urgently respond to the situation, and at this time, both the company and the relevant responsible persons have been exposed to legal risks, and it is difficult to recover losses. In order to reduce the occurrence of such a situation, as a professional department of risk prevention and control of the company - the Legal Department, it is urgent to improve the company's governance structure and internal control system in the ordinary work, and continue to improve the company's directors and supervisors of the awareness of compliance and compliance capabilities, the formation of the full-process compliance mechanism of pre-emptive prevention, monitoring, and disposal of the aftermath of the incident.
II
Duty of Care and Risk Isolation of Directors and Supervisors of Listed Companies

Mr. Zhao Qilong
Mr. Zhao Qilong, Senior Partner of King&Capital, introduced the provisions and requirements of the Company Law, Securities Law and relevant judicial interpretations on the rights and obligations of the directors and supervisors of listed companies through the introduction of the cases of Kangmei Pharmaceuticals, Leshi.com Misrepresentation and Kangdexin and introduced the risk isolation measures of the directors and supervisors of listed companies in the process of performance of their duties, and the sharing of Mr. Zhao played a considerable guidance role in the compliance of the legal affairs. Mr. Zhao's sharing is a great guide for legal compliance work. The following is a brief summary of Mr. Zhao's presentation:
(I) Requirements of the Company Law on the Duty of Faithfulness and Diligence of Company Directors and Supervisors
1. Duty of loyalty
The duty of loyalty is the minimum obligation and standard for company directors and supervisors, and is a requirement for their character and virtue. Directors and senior management shall not place their own interests above the interests of the company and shareholders, and shall not utilize their authority for their own benefit, which is specifically manifested in self-dealing, connected transactions, management remuneration, corporate opportunities and competition in the same industry.
2. Duty of diligence
The standard of duty of diligence can be summarized in ten words, namely, "good faith, attention, the best interests of the company". In the course of performing their duties, the directors and supervisors of the company shall have no interest in the contents of their business judgment, shall have reasonable grounds to believe that the information they possessed at the time about their business judgment is sufficient, appropriate and reliable (such as legal opinions of attorneys, reports of accounting firms, and market research reports), and shall have reasons to believe that their business judgment is in the best interests of the company. If the following behaviors exist in the course of the company's operations, it may be found to be a violation of the duty of diligence, (1) not asking questions about the company's specific operations, (2) making hasty decisions, (3) voting on a board resolution without conscientiousness and not adhering to one's own opinion, and (4) not exercising the right to know.
Among them, the standard of due diligence refers to the duty of care of a good administrator, which in turn includes two aspects, namely, work ability and work attitude. To judge whether the duty of diligence has been exercised, the rule of business judgment is generally adopted, and the rule of business judgment (business judgment rule) is subject to the principle of three simultaneous, i.e., the same person under the same conditions will make the same decision.
(ii) Characteristics of the Duty of Care of Directors and Supervisors of Listed Companies
The operation and management of listed companies, especially its controlling shareholders, de facto controllers and directors and supervisors of the faithfulness and diligence will directly affect the interests of ordinary shareholders, improve the supervision of the major shareholders, de facto controllers and senior management, regulation of "insiders" is to maintain the stable development of the capital market is an important means.
1. Duty of care of controlling shareholders and de facto controllers (emphasis)
Controlling shareholders and de facto controllers of listed companies are the representatives of the company's interests and the initiators of the company's decision-making, and they need to have the duty of good faith, and shall not utilize their controlling position to harm the interests of the company and other shareholders.
2. Duty of care of executive directors, supervisors and senior management (medium)
Executive directors, supervisors, and senior management personnel may differ by full-time or part-time employment, and also by the authority to perform their duties (supervisor and oversight).
3. Duty of care for independent directors (light)
Independent directors are generally part-time, in terms of liability to be appropriate to their remuneration, and independent directors can reduce or exempt themselves from the corresponding liability by relying on the professional advice of a third party.
(iii) Risk prevention or exemption from liability of company directors and supervisors
First, directors and officers can be exempted from liability on the grounds that they have done their best to fulfill the rules of business judgment; second, one way to address the risk prevention of directors and officers is to purchase directors' and officers' liability insurance coverage, which consists of two parts: 1) insurance company to pay on behalf of a director or officer when the director's and officer's losses cannot be compensated from the company in which the director or officer is employed; and 2) company indemnification insurance to cover losses of directors or officers when the company legally compensation for the loss of its directors or officers, then the insurance company pays the loss on behalf of the company. Again, it is recommended that legislation be enacted to set a cap on the compensation of directors and officers with reference to the spirit of the labor law, so as to avoid excessive liability for compensation that would discourage directors and officers from their positions and affect the governance structure of the company.
III
Legal Risks Related to Transfer of Benefits Behavior of Company Executives for Similar Operations and Other Benefits

Mr. Sun Yanhui
King&Capital senior partner Sun Yanhui takes the transfer of benefits such as the same kind of operation by company executives as the starting point, and provides the company with the way to prevent and solve the same business competition through the meticulous analysis of the same business competition behavior.
(A) what is the competition
At present, there are two main criteria for the determination of "the same kind of business" in the process of judicial practice, one is to determine whether the business scope of the company's registration belongs to "the same kind of business", and if the business scope of the two companies is the same, it constitutes the same business; one is to determine whether the actual business activities and business behavior of the two companies are the same; the other is to determine whether the actual business activities and business behavior of the two companies are the same. The first is to determine whether the actual business activities, business behavior constitute the same kind of business. Therefore, in practice, we can adopt different determination standards according to the different identities of the plaintiff and the defendant, in order to safeguard the interests of the company.
In practice, there is no uniform standard for determining the criteria of "self-employment" and "operating for others". Some courts consider that the establishment of other companies initiated by the directors and senior management, or their direct or indirect holding of equity interests in other companies constitutes competition in the same business; some courts consider that the perpetrator's activities in the same business constitute competition in the same business; and some courts consider that the perpetrator's activities in the same business constitute competition in the same business. Some courts have held that a director or senior executive who initiates the establishment of another company, or directly or indirectly holds equity in another company, constitutes a competitor; some courts have held that the actor is only a "general shareholder" of the competing company, which does not constitute self-employment.
(ii) How to Calculate Attributable Income
Combined with the relevant cases, there are three main ways of calculating the attributable income in practice, namely (1) the salary, bonus and dividends obtained by the directors and senior management from the competing company should be attributed to the company; (2) the equity premium obtained by the directors and senior management from the sale of equity interests in the competing company can also be attributed; and (3) the profits of the competing company are also attributable to the company, and should be calculated by multiplying them with the percentage of shareholding of the directors and senior management. (3) Profit from a fellow company is also attributable income, which should be multiplied by the percentage of shareholding of directors and officers.
In summary, Mr. Sun advocated that different persons in the company should be treated differently, i.e., if the directors and senior management are the controlling shareholders or actual controllers, and can control the intermediate company, the part of the company's profit corresponding to the equity/shareholding of the director/senior management should be recognized as the income; if the director/senior management are only involved in part of the operation, the calculation should be made according to the actual income of the director/senior management. .
The right of imputation should be the first and foremost mode of liability for breach of the duty of fidelity, but due to the existence of the infringer's income is difficult to calculate or insufficient to make up for the company's losses, therefore, for the parties to advocate two modes of liability, should give priority to the application of the right of imputation, and in the case of failure to protect the company's interests through the right of imputation, can be taken to compensate for the loss of the mode of liability, but should pay attention to the interests of the company to safeguard the balance of the liability and the liability for compensation. However, attention should be paid to the balance between the protection of the company's interests and the liability for compensation.
(iii) Difference between competition and restriction of non-competition
The main difference between competition and restriction of non-competition is reflected in the following aspects, first, the applicable legal basis is different, competition applies to Article 148 of the Company Law, restriction of non-competition applies to Article 23 of the Labor Contract Law; second, the applicable subject is different, competition applies to the directors and senior management, restriction of non-competition applies to the workers who are bound by the labor contract and have the obligation of confidentiality; Third, the binding time is different, the same competition basically applies to directors and senior management personnel during their term of office, but there are exceptions that they still need to assume the corresponding obligations after the end of their term of office, and the restriction on non-competition applies to the termination or termination of the labor contract, but the duration of the restriction on non-competition shall not be more than two years; fourth, the different procedures, in general, the competition is not subject to the arbitration of the pre-arbitration of labor disputes, and the restriction on non-competition requires First labor dispute arbitration prior to the procedure.
(IV) Preventive Measures and Solutions for Competition in the Same Industry
In order to prevent the directors and senior management from engaging in the same business competition behavior, the company can restrict all the shareholders or senior management from engaging in the same business competition in the articles of association or shareholders' agreement, and agree in detail on the liability for breach of contract with operability, in addition, if it is not possible to be restrained by way of the articles of association or shareholders' agreement, it can also be adopted in the form of a letter of commitment. When the act of interbank competition has occurred, the competing party may be required to issue a written undertaking to make a request to avoid competition and conflict of interest, or to concentrate the competing business into the company or the competing party's operation through practical ways, or to require the competing party to undertake to complete the change of business scope within a period of time, or to transfer it to an unaffiliated third party in case of non-completion of the change.
In the context of the current reform of the compliance and non-prosecution system for companies involved in cases, corporate executives need to understand the risks involved while fulfilling their duties of loyalty and diligence to the company. Enterprises should also help executives to understand their legal responsibilities and build an internal compliance management system. King&Capital Law Firm has carried out multi-dimensional exploration and practice in the business of corporate compliance, and accumulated a lot of research results and rich practical experience. King&Capital Law Firm team will protect the healthy development of enterprises with its excellent professional ability and responsible working attitude.