At 14:00 on May 13, 2025, the salon on the subject of intellectual property crime in the context of the new judicial interpretation of intellectual property crime was held on schedule in the multifunctional hall on the 22nd floor of Beijing King&Capital Law Firm.

The meeting was presided over by Lv Yan, Deputy Director of King&Capital Food and Drug Law Research Center, who firstly expressed his warm welcome and heartfelt thanks to all the guests. After the conclusion of the Third Food and Drug Environmental Intellectual Property Crime Governance Forum on April 20 this year, the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate issued issued the Interpretation on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in Handling Criminal Cases of Infringement of Intellectual Property Rights on April 24th. He introduced the King&Capital Food and Drug Law Research Center as a platform specializing in the study of environmental food and drug know-how, and organized nine researchers of the Center from all over the country and different law firms to share their views on the Interpretation and issues related to intellectual property crimes.
I. Opening Remarks

Mr. Tang Jianbin, Director of King&Capital Food and Drug Law Research Center, delivered a speech. He said that King&Capital Food and Drug Law Research Center was founded on the basis of King&Capital Law Firm with strong openness, and hoped to build the platform into a cross-firm, cross-regional open platform to unite the excellent lawyers in the country of environment, food and drug knowledge, and to jointly study and publish the research results. The center in the “food and drug crime case manual” “environmental crime theory exploration and practice essence” and other two bibliography, based on this year, further formed “food enterprise administrative criminal law risk prevention and control and compliance” “drug enterprise administrative criminal law risk prevention and control and compliance” “intellectual property rights crime typical case analysis and defense strategy” and other monographs. Subsequently, Mr. Tang Jianbin talked about some of the highlights of the new judicial interpretation of intellectual property criminal cases from a macro point of view, and wished this salon a successful outcome.
Second, the first half of the keynote speech

Zhang Sijia lawyer shared the theme of “from an innocent case to talk about the defense of infringement of trade secrets”, she combined with her own handling of an innocent case of infringement of trade secrets, analysis of criminal defense points. She emphasized that the appraisal opinion is the focus of the review of the defense, to determine whether a technical information meets the elements of trade secrets, pay attention to the review of the information is not known to the public at the time of infringement, infringement of the occurrence of the necessary confidentiality to determine the right to claim that the information constitutes a trade secret. Zhang Sijia also mentioned that we should also pay attention to the market changes with the specific case, and be good at using the market changes as the intervening factor to cut off (or doubt) the causal relationship between the infringement and the consequences of the damage. In addition, she also shared the practical difficulties in distinguishing between technical secrets and carriers, causality argumentation, etc., and suggested strengthening the evidence defense through the expert-assisted person system, which provided a practical path for the innocent defense and compliance review of intellectual property crime cases.

Ms. Jin Fenghua shared the topic of “Civil, Administrative and Criminal Intersection of Intellectual Property Rights (Trade Secret Crimes as an Example)”, in which she combined the latest judicial interpretations to analyze the differences between civil, administrative and criminal legal relations in terms of adjustment object, normative purpose and behavioral elements, and emphasized the application of the principle of unity of law and order in the protection of intellectual property. Regarding the protection of trade secrets, Jin Fenghua compared the procedural characteristics and evidence standards of civil, criminal and administrative reporting, combined with the Civil Code, the Anti-Unfair Competition Law and other laws and regulations, explored the disputes over ownership, evidence collection and other practical issues, and explained the application of the scenarios of criminal-civil parallelism and civil first, criminal later through typical cases. The salon provided a practical path of procedural choice and legal application for solving the intersection problems of civil and criminal law in intellectual property cases, and helped to enhance the effectiveness of comprehensive protection of intellectual property rights.
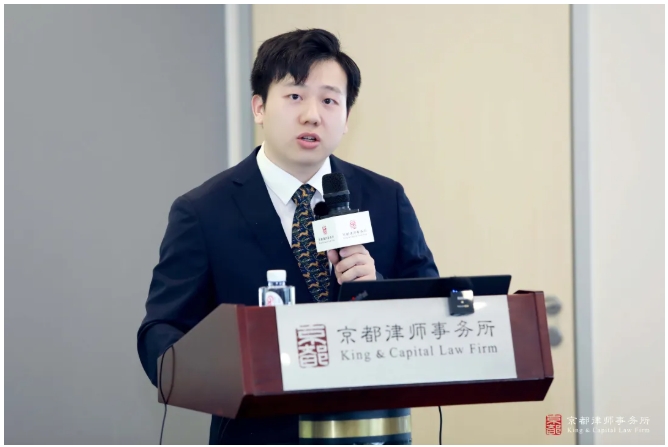

Mr. Wang Siyu shared the topic of “Revision and Interpretation of the New Judicial Interpretation on the Crime of Counterfeiting Registered Trademarks”, pointing out that the new interpretation for the first time explicitly included “service mark” in the scope of protection of the crime of counterfeiting registered trademarks, and refined the definition of “the same kind of goods and services” and “the same trademark”. He pointed out that the new interpretation explicitly includes “service mark” in the protection scope of the crime of counterfeiting registered trademark for the first time, and refines the identification criteria of “the same goods and services” and “the same trademark”, e.g., changing the font and color of the trademark may constitute infringement. With regard to sentencing standards, Wang Siyu emphasized that the threshold for service mark infringement is RMB 50,000 yuan of illegal income, and the amount of infringement of goods and service marks can be calculated together. In the crime of selling counterfeit goods, situations such as “buying and selling at a low price without justifiable reasons” and “transferring evidence” can be presumed to be “knowingly”, while lowering the quantitative standard for the crime of illegally manufacturing trademark marks to 10,000 pieces. At the same time, it lowered the quantitative standard for the offense of illegal manufacture of trademark signs to 10,000 pieces. Combined with the difficulties in judicial practice, the salon provided guidelines on the application of the new rules for the accurate identification and defense of trademark crimes, and helped to enhance the standardization and effectiveness of criminal protection of intellectual property.
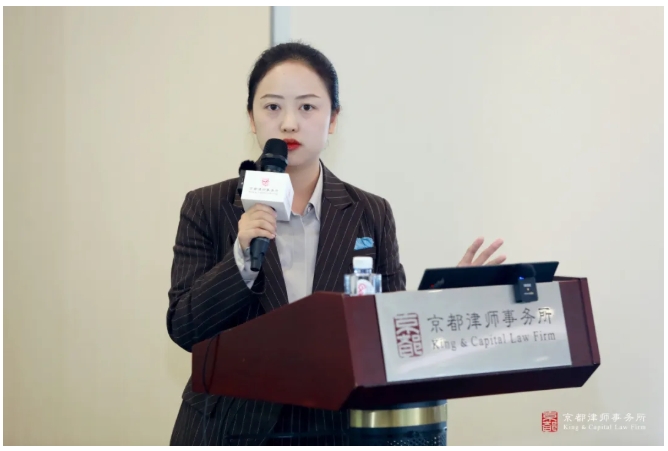

Ms. He Shunqi shared the topic of “How to Judge the Authenticity of the Goods Involved in Trademark Crime Cases”. She combined the criminal law and judicial interpretations to determine the authenticity of the goods involved in a trademark crime case from the three core elements of “whether it is licensed by the owner of the trademark”, “whether it is the same trademark”, “whether it is the same goods” and “whether it is the same kind of goods”. She started from the three core elements of “whether it is licensed by the trademark owner”, “whether it is the same trademark” and “whether it is the same kind of goods”, analyzed the practical problems of collateral goods and parallel importation, and emphasized that collateral goods are still genuine goods if the trademark logo has not been tampered with, and that parallel importation does not constitute a crime if it conforms to the principle of exhaustion. He Shunqi pointed out through cases that “identical trademarks” need to meet the requirements of “identical” or “basically indistinguishable and sufficient to mislead the public”, such as changing fonts, colors, and other minor adjustments may constitute The “same kind of goods” should be judged in conjunction with the Nice Classification, functions and raw materials, etc., and the use of trademarks beyond the approved scope does not constitute a crime. The salon provided refined guidelines for the examination of evidence and defense of trademark crime cases, and helped to accurately differentiate between civil infringement and criminal offense in judicial practice.
III. Award of Appointment Letter
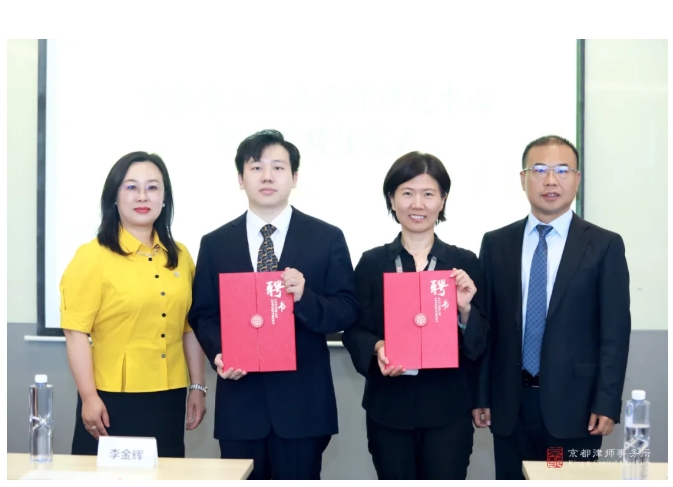

The official agenda of the salon included the appointment ceremony of the researchers of King&Capital Food and Drug Law Research Center. Two lawyers, Jin Fenghua and Wang Siyu, were appointed as researchers of King&Capital Food and Drug Law Research Center. Mr. Tang Jianbin, Director of King&Capital Food and Drug Law Research Center, and Mr. Zhang Sijia, Deputy Director and Secretary General of the Center, presented them with appointment certificates and took a group photo.
Fourth, the second half of the keynote speech
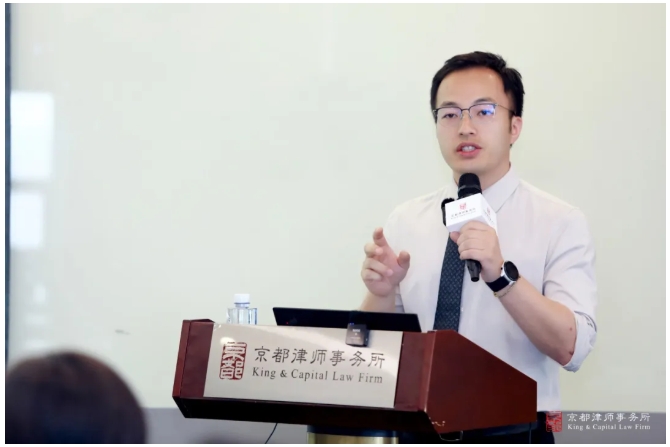

Mr. Xu Wei shared the topic of “Issues Related to the Calculation of the Amount of Loss for the Crime of Infringing on Trade Secrets”, which explained in depth the latest judicial interpretations of the “aggravating circumstances”, analyzed the rules of calculation of the “amount of loss” in different infringement scenarios (such as the reasonable license fee, loss of profits, commercial value) and the calculation of the “amount of loss” in different infringement scenarios. He also analyzed the calculation rules of “amount of loss” in different infringement scenarios (such as reasonable license fee, loss of profit, commercial value, etc.), and explained the overall determination of the value of trade secrets, the review of the relevance of R&D costs, and the logic of determination of the illegal income through the typical cases of Chen Moumou case and Ye Moumou case. Xu Wei emphasized that in judicial practice, it is necessary to distinguish whether the trade secrets are public or lost, and strictly review the relevance of the appraisal opinion, which provides practical guidelines for the judicial determination of trade secret infringement cases and the criminal compliance of enterprises, and helps balance the protection of intellectual property rights and the protection of the rights and interests of enterprises.

Li Jinhui shared the theme of “about food, drug, environment and knowledge of criminal incidental civil public interest litigation,” he combined with the “people's procuratorate public interest litigation rules”, analysis of public interest litigation clues, fulfillment and typical cases, focusing on the production and sale of ordinary commodities is applicable to the incidental civil public interest litigation, the perpetrator of the operator, upstream and downstream offenders. It focuses on whether the production and sale of ordinary commodities is applicable to incidental civil public interest litigation, whether the perpetrator is an “operator”, whether the upstream and downstream offenders bear punitive damages and other controversial issues. Li Jinhui pointed out that, food and drug safety in the field of consumer rights and interests of the crime, the procuratorate can file a criminal attached to civil public interest litigation, claiming three times punitive damages and public apology. Combined with practical difficulties, the salon provided ideas on the applicable boundaries and responsibility determination of public interest litigation in intellectual property crime cases, and helped strengthen the interface between criminal protection of intellectual property and social public interest relief.

Mr. Lu Xianghui shared the topic of “The concept of ‘strict protection’ from the ‘knowledge’ presumption rule in the new judicial interpretation of intellectual property rights”, which centered on the “knowledge” presumption and counter-evidence in the crime of selling counterfeit registered trademark goods. He analyzed the “alteration of trademark”, “low price of goods” and “transfer of evidence” in combination with the “Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law to the Handling of Criminal Cases of Infringement of Intellectual Property Rights”. ”, “transfer of evidence” and other six categories of presumptive “knowledge” of the situation, emphasizing the need for comprehensive evidence in judicial practice to determine the subjective knowledge, allowing the perpetrator to overturn the presumption through counter-evidence, and combined with typical cases (such as Zhang Yefeng case. Zheng Jinfang case) to explain the defense of the case, Zheng Jinfang case) to explain the key points of defense and corporate compliance path. The salon provided theoretical and practical references for the subjective determination of intellectual property crimes and enterprise risk prevention and control in judicial practice, helping to balance intellectual property protection and criminal justice.

The topic shared by Ms. Wei Kun is “Brief Legal Analysis of Counterfeit Imported Cosmetics Case”, she combined with the PPT of Lu Moumou and other counterfeiting registered trademark case to develop in-depth interpretation, and disclosed in detail that the criminal group made and sold counterfeiting “LANCOME” “DIOR” and other brands of cosmetics by renting stores to affix labels and selling through the Jitterbug store between 2019 and 2021, with a total amount of over 145 million RMB involved in the case, The amount of money involved exceeded 145 million yuan, and the illegal proceeds amounted to 37 million yuan. The analysis centered on core issues such as the legal application of “particularly serious circumstances” in the characterization of the case, the full chain of common crimes (e.g. Chen, the storage provider, was found to be an accomplice), and the difference in sentencing between principal and subordinate offenders (the principal offender, Lu Moumou, was sentenced to 8 years' imprisonment and punished with a fine of 20 million yuan), etc., and emphasized that the e-commerce platform needs to strengthen the auditing mechanism, the brand side should strengthen the monitoring of trademarks and that the consumers can report the case through the 12315 platform and advocate for refund of the amount of money and compensation. The analysis emphasizes that e-commerce platforms need to strengthen audit mechanisms, brands should strengthen trademark monitoring, and consumers can report and claim a refund through the 12315 platform.

Mr. Guo Jianming shared the topic of “Analysis of the rules for determining the amount of ‘illegal income’ in intellectual property crimes”, he analyzed the relationship between illegal income and Article 64 of the Criminal Law “Recovery of all property”, analyzed the impact of illegal income on sentencing and fines, and finally talked about his own understanding of the interface between execution and punishment in the handling of intellectual property cases. Finally, he talked about his understanding of the convergence of execution and punishment in the handling of intellectual property cases.
The salon was successfully held, which provided important reference for the identification of intellectual property crimes and multi-dimensional co-rule in judicial practice.

Translated with DeepL.com (free version)